Protect your family from respiratory illnesses. Schedule your immunization here >
Ranked nationally in pediatric care.
Arkansas Children's provides right-sized care for your child. U.S. News & World Report has ranked Arkansas Children's in seven specialties for 2025-2026.

It's easier than ever to sign up for MyChart.
Sign up online to quickly and easily manage your child's medical information and connect with us whenever you need.
We're focused on improving child health through exceptional patient care, groundbreaking research, continuing education, and outreach and prevention.

When it comes to your child, every emergency is a big deal.
Our ERs are staffed 24/7 with doctors, nurses and staff who know kids best – all trained to deliver right-sized care for your child in a safe environment.

Arkansas Children's provides right-sized care for your child. U.S. News & World Report has ranked Arkansas Children's in seven specialties for 2025-2026.

Looking for resources for your family?
Find health tips, patient stories, and news you can use to champion children.

Support from the comfort of your home.
Our flu resources and education information help parents and families provide effective care at home.

Children are at the center of everything we do.
We are dedicated to caring for children, allowing us to uniquely shape the landscape of pediatric care in Arkansas.

Transforming discovery to care.
Our researchers are driven by their limitless curiosity to discover new and better ways to make these children better today and healthier tomorrow.

We're focused on improving child health through exceptional patient care, groundbreaking research, continuing education, and outreach and prevention.
Then we're looking for you! Work at a place where you can change lives...including your own.

When you give to Arkansas Children's, you help deliver on our promise of a better today and a healthier tomorrow for the children of Arkansas and beyond

Become a volunteer at Arkansas Children's.
The gift of time is one of the most precious gifts you can give. You can make a difference in the life of a sick child.

Join our Grassroots Organization
Support and participate in this advocacy effort on behalf of Arkansas’ youth and our organization.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.

Learn How We Transform Discovery to Care
Scientific discoveries lead us to new and better ways to care for children.
When you give to Arkansas Children’s, you help deliver on our promise of a better today and a healthier tomorrow for the children of Arkansas and beyond.
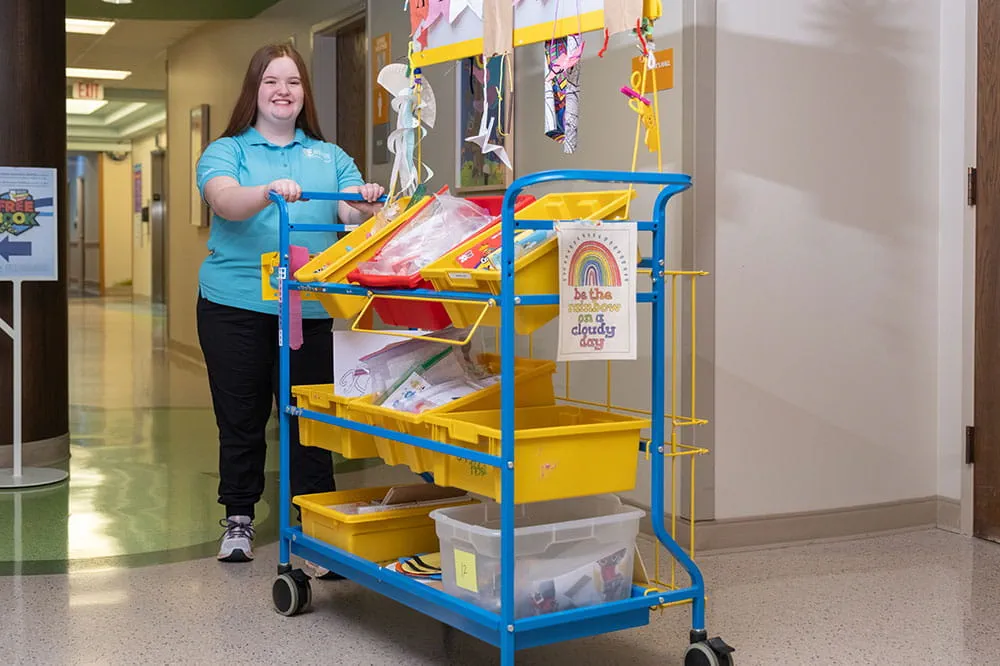

Your volunteer efforts are very important to Arkansas Children's. Consider additional ways to help our patients and families.
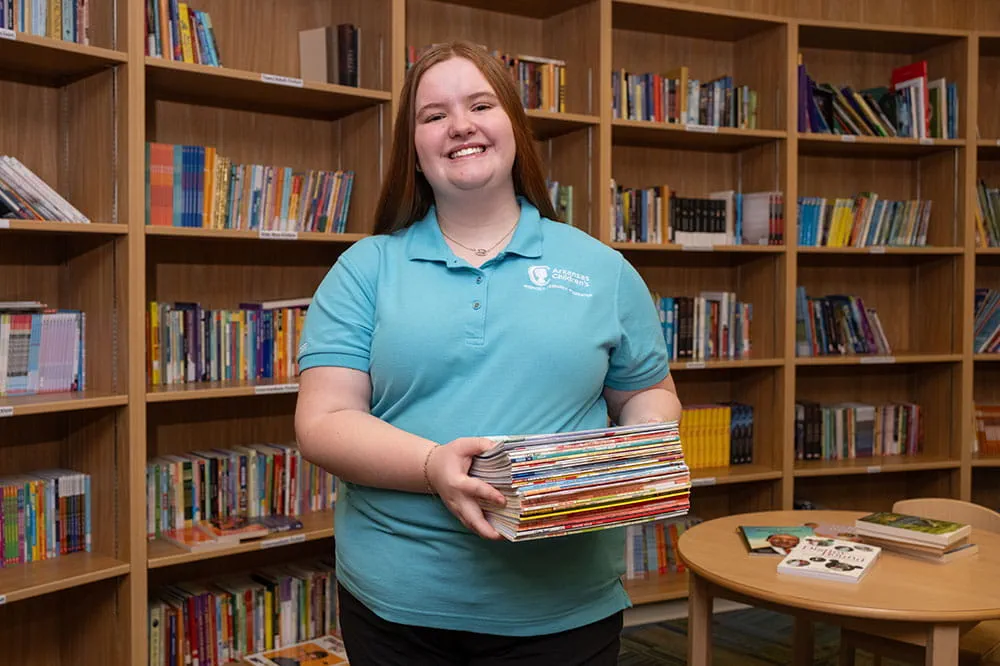

Join one of our volunteer groups.
There are many ways to get involved to champion children statewide.
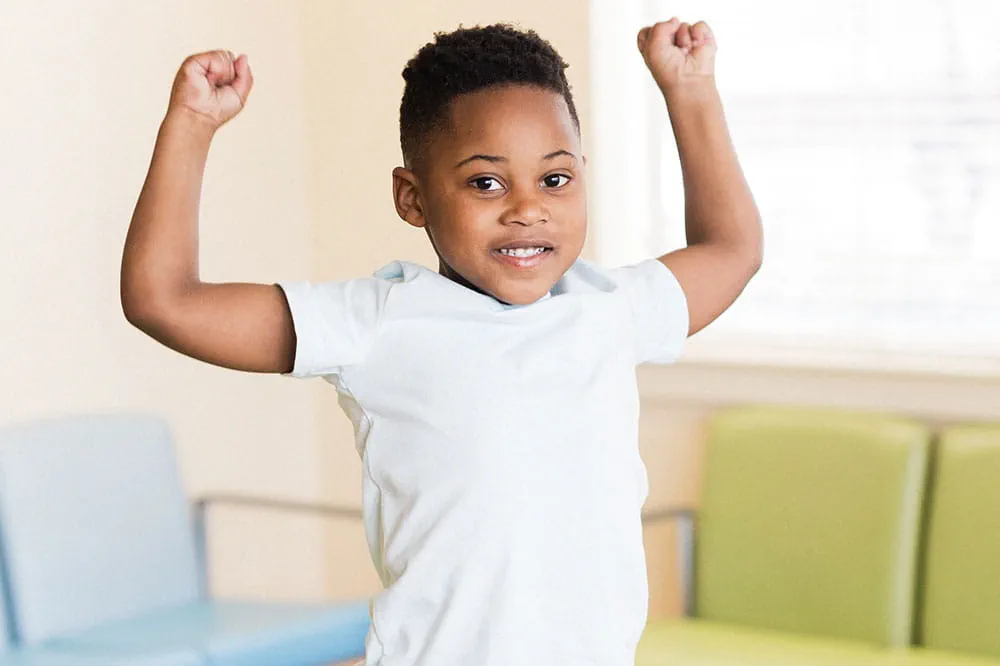

Make a positive impact on children through philanthropy.
The generosity of our supporters allows Arkansas Children's to deliver on our promise of making children better today and a healthier tomorrow.
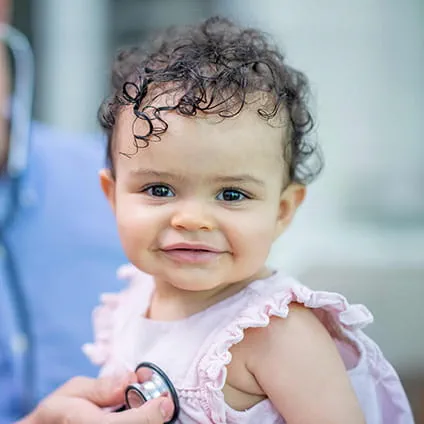

Read and watch heart-warming, inspirational stories from the patients of Arkansas Children’s.

Hello.

Arkansas Children's Hospital
General Information 501-364-1100
Arkansas Children's Northwest
General Information 479-725-6800

Glossary of NICU Terms
Below is a comprehensive list of terms you will possibly hear while you infant is in the NICU at Arkansas Children's.
- Anemia
- Apnea
- Asphyxia: When the body does not receive enough oxygen
- Bassinet: Open crib that does not provide heat source
- Birth defect
- Bolus: Feeding volume given in one setting similar to a meal, instead of over a period of time or continuously.
- Bradycardia (Brady): A temporary slowing of the heart rate. Gentle touching of the baby is usually enough to raise the heart rate.
- Central line (CVL)
- Cerebral palsy (CP): A result of damage to the brain that can cause abnormal movements and other developmental delays.
- Chronic lung disease (CLD)
- Cleft lip and palate: An abnormal opening in the lip and/or roof of the mouth that can cause feeding, dental, and speech problems. Most require eventual surgical repair.
- Congenital heart defect
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
- Desaturation (Desat): When there is too little oxygen reaching the tissues of the body. This may cause the skin to appear blue or gray. A machine called a pulse oximeter (pulse ox) measures the oxygen level.
- Diaphragmatic Hernia: A hole in the muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen (diaphragm). This hole (hernia) allows the bowel to push up into the chest cavity. This can keep the lungs from growing and functioning properly. It can interfere with the baby's breathing, circulation and oxygenation.
- Duodenal Atresia: A blockage of the upper portion of the small bowel that can cause abdominal swelling and vomiting. Most require surgical repair.
- Endotracheal tube (Breathing tube)
- Gastroschisis: A defect in the abdomen which the can affect the bowel, stomach, and liver causing them to form on the outside of the body.
- Hydrocephalus: Abnormal growth of the head related to a blockage in the brain or spinal cord that causes cerebral spinal fluid to build-up in the head. It usually requires placement of a shunt to allow built-up fluid to drain.
- Infection or Sepsis
- Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)
- Isolation: Use of gown, gloves, or mask to help prevent the spread of infection. Personal protective equipment (PPE) may be required to prevent the spread of infection when entering a patient room or treating a patient.
- Isolette or Incubator
- Jaundice
- Kangaroo care (Skin to Skin)
- Meconium aspiration syndrome: When the baby breathes in the dark green substance produced in the bowels while still inside mom. This can irritate lung tissues and block airways in the lungs making it very difficult for the baby to breathe.
- Monitor
- Multipurpose room: Rooms used for parents to spend the night and learn to care for the infant when they are close to going home. May be used for other purposes as determined by individual patient/family needs.
- Myelomeningocele: When the spinal column does not form properly. A gap in the bony parts of the spine may allow spinal tissue to push out through the skin. The baby may have some loss of feeling or movement in the legs. Babies may also have loss of bowel and bladder control depending on the severity of the defect.
- Nasal cannula
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
- “Nothing by mouth” (NPO): Baby cannot take any liquid or food into its mouth. Premature and/or sick babies may have trouble digesting their milk and may be placed NPO to give their system time to rest or heal.
- Omphalocele: When some of the contents of the abdomen push out the umbilical cord. A sac usually covers the abdominal contents.
- Orogastric tube (OGT)/ Nasogastric tube (NGT): A tube placed in the mouth or nose that goes into the stomach. Used for feeding or removing air or contents from the stomach.
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
- Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension (PPHN)
- Peripheral intravenous line (PIV)
- Premature newborn: A baby who is born before 38 weeks of pregnancy are completed.
- Pulse oximeter (pulse ox): Monitoring the amount of oxygen reaching the body's tissues through the baby's skin.
- Residuals: The amount of milk found in the stomach before it is time to give the next feeding. Nurses will check for residuals through a feeding tube before starting a new feeding.
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)
- Room Air: The air we breathe contains 21% oxygen among other components.
- Rooming In: When families spend the night and focus on learning to care for their baby independently
- Seizures: When the electrical signals in the brain do not work properly.
- Therapy – Occupational (OT), Speech (ST), Physical (PT):Therapies prescribed for babies based on their individual needs
- Total parenteral nutrition (TPN): Intravenous fluids that provide nutrition when the infant is not able to tolerate all their feedings through the stomach. It includes fluid, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF): An abnormal passage or connection between the windpipe (trachea) and the food pipe (esophagus). This connection can make feeding difficult. Most require surgical repair.
- Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN): When there is a delay in the absorption of lung fluid after birth. The baby may breathe fast until the fluid clears from the lungs.
- Transpyloric tube (TPT): A tube placed in the mouth or nose that goes past the stomach. Used for feeding babies that cannot tolerate food in the stomach.
- Umbilical line (UAC/UVC)
- Ventilator (vent)
- Warmer

